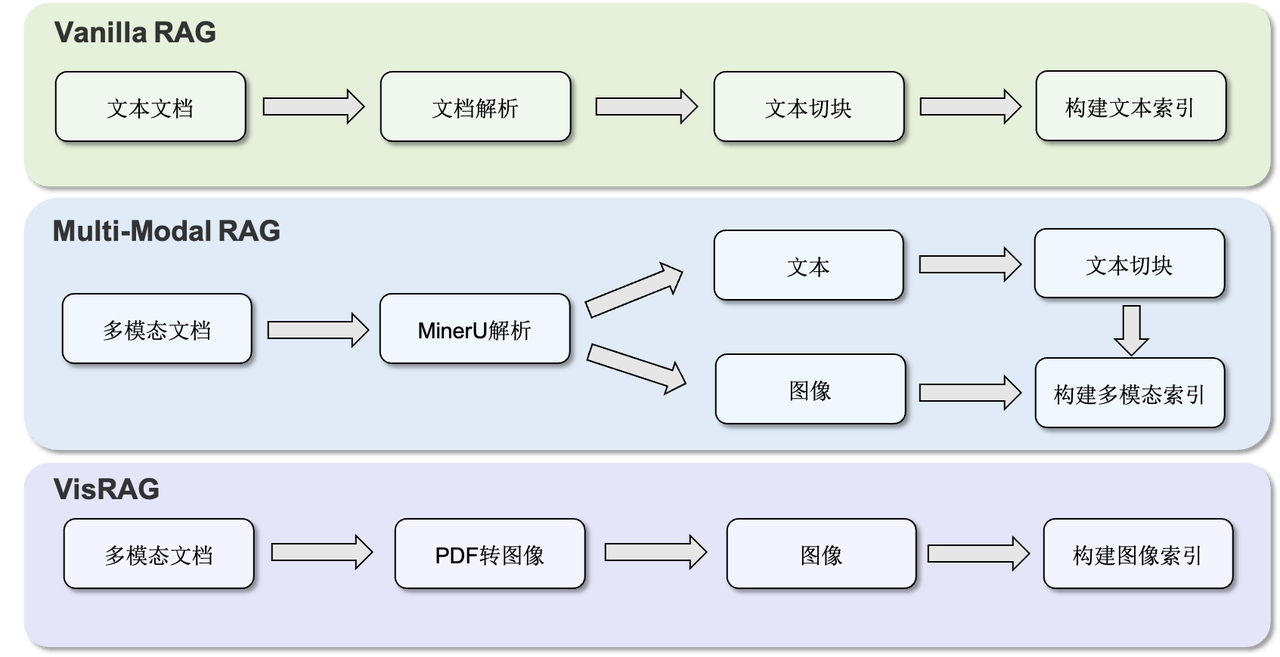
UltraRAG 3.0: No More Black Boxes, Full Transparency in Reasoning
"Validating an algorithm prototype takes a week, but building a usable system takes months." This seemingly sarcastic quip is the real predicament every algorithm engineer must face.
Today, Tsinghua University's THUNLP Lab, Northeastern University's NEUIR Lab, OpenBMB, ModelBest and AI9Stars jointly release UltraRAG 3.0, addressing these pain points with a developer-centric technical framework featuring 3 core advantages:
-
One-click leap from logic to prototype, letting algorithm engineers focus on "algorithms": Provides a "what you see is what you get" Pipeline builder that automatically handles tedious interface encapsulation. Just focus on logic orchestration, and static code instantly becomes an interactive demo system.
-
Full-chain white-box transparency, "pixel-level" visualization of reasoning traces: Creates a "transparent" reasoning verification window, presenting in real-time every loop, branch, and decision detail of the model during complex long-chain tasks.
-
Built-in intelligent development assistant, your "interactive development guide": Embeds an AI assistant that understands the framework, assisting in generating Pipeline configurations and optimizing Prompts through natural language interaction, greatly lowering the barrier to entry.
Logic as Application — A "Zero-Distance" Experience from Orchestration to Interaction
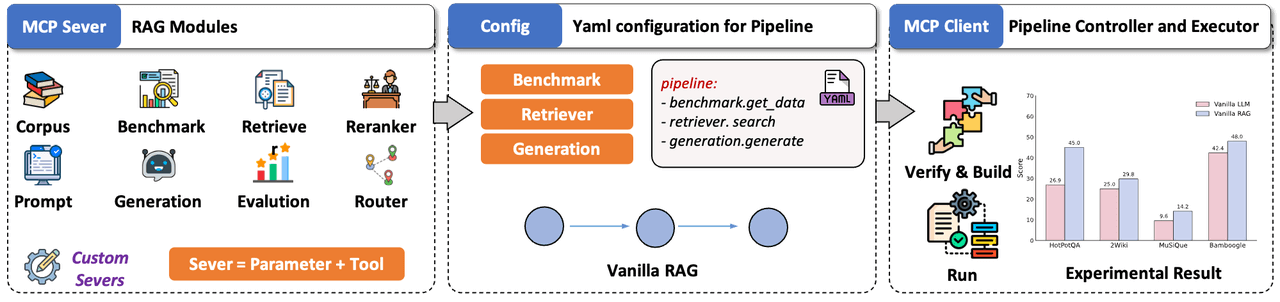
Let the endpoint of algorithms no longer be cold console logs. UltraRAG 3.0 automatically handles tedious interface encapsulation and parameter integration, ensuring that the moment logic orchestration is complete, an interactive demo interface is simultaneously generated:
- Configuration as Application: Simply define the Pipeline's YAML configuration file, and the framework automatically parses and transforms it into a standard interactive Demo.
- Dual-Mode Builder: To balance ease of use and flexibility, we've built a construction engine with real-time synchronization between visual and code modes:
- Canvas Mode: Intuitively assemble complex logic like Loop and Branch through UI components, like building blocks.
- Code Mode: Directly edit YAML configuration files with the canvas view rendering updates in real-time, meeting developers' needs for precise parameter fine-tuning.
- One-Click Build & Verify: After construction, click the "Build" button at the top. The system automatically performs logic self-checks and syntax validation, dynamically generating parameter configuration panels. The instant parameters are ready, static algorithm logic instantly transforms into an interactive system, truly achieving "what you write is what you get, what you get is what you use."
Reject "Black Boxes" — Making Complex RAG Reasoning Traces Clearly Visible
As RAG technology evolves from simple single-round retrieval to multi-round dynamic decision-making, reasoning chains often extend to hundreds of Steps. Without intermediate state monitoring, the debugging process is like starting over in the fog, with error localization relying entirely on "guessing."
UltraRAG 3.0 redefines the Chat interface — it's not just the user interaction entry point, but also a logic verification window. We deeply understand that for developers, knowing "what the result is" is far from enough; seeing "how the result came about" is the key to optimization.
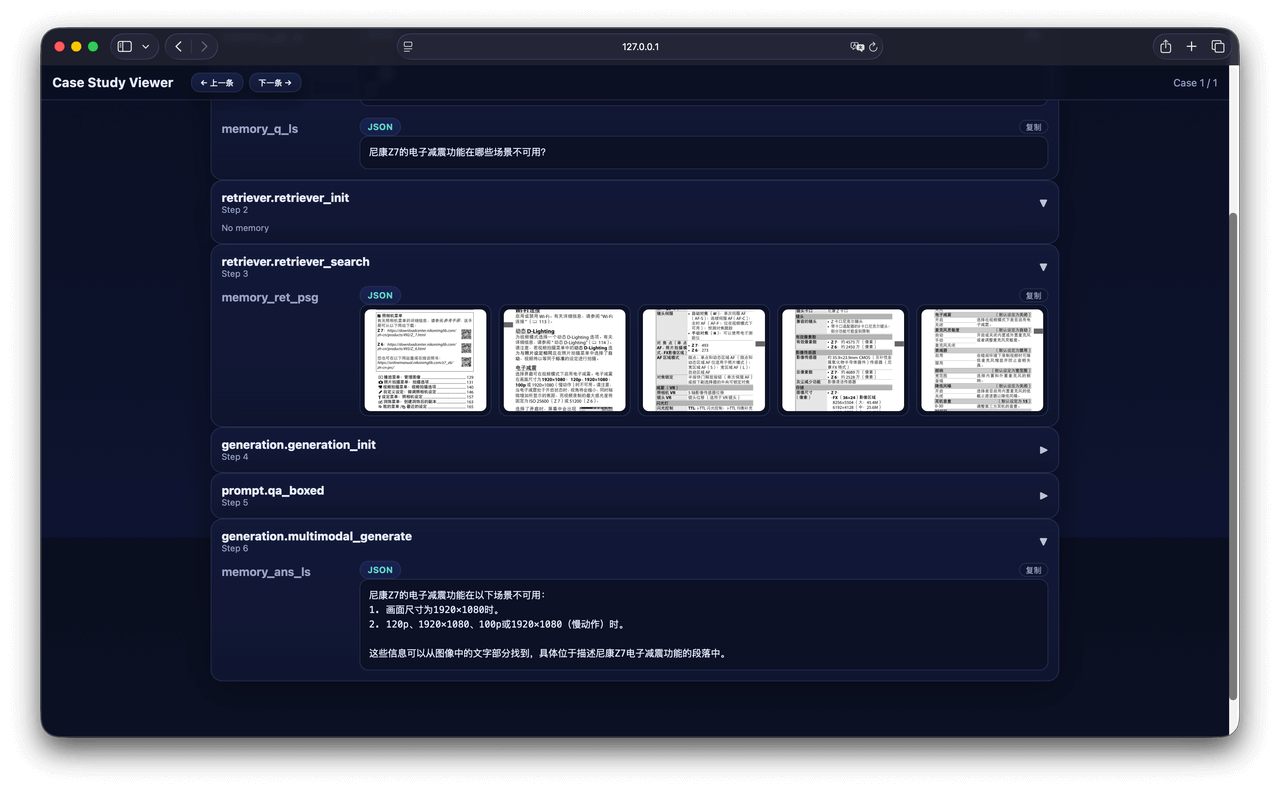
Through the "Show Thinking" panel, we provide pixel-level real-time visualization of the system's entire "thinking" process — from complex loop branches to specific tool calls, all intermediate states are presented in a structured streaming format. Even for complex long-process tasks like DeepResearch, developers can track execution progress in real-time, making the process no longer a dark wait. When Bad Cases appear, developers no longer need to dig through backend logs; they can directly compare retrieval slices with final answers on the interface, quickly determining whether the problem lies in "data layer noise" or "model layer hallucination," greatly shortening the optimization iteration cycle.
Here we selected two typical scenarios from the AgentCPM-Report workflow to demonstrate the practical effects of "white-box" debugging:
Breaking Free from "Framework Shackles" in Custom Development
Wanting to try a new algorithm logic often requires diving deep into the framework's internals and rewriting large amounts of inherited classes. To achieve 10% core algorithm innovation, one has to bear 90% of framework learning costs.
UltraRAG 3.0 embeds the entire development documentation and best practices into the framework's built-in intelligent assistant. While it may not help you write an entire project like Cursor, it is absolutely the most efficient assistive tool that understands UltraRAG. Through natural language interaction, it helps you completely bridge the cognitive gap between "reading documentation" and "writing configurations":
- Configuration Generation: Just describe your requirements (e.g., "I want a pipeline with multi-way recall and reranking"), and the assistant automatically generates a standard Pipeline structure draft that can be used directly with minor adjustments.
- Prompt Tuning: The assistant provides targeted Prompt optimization suggestions based on the current task context, quickly adapting to specific business scenarios.
- Understanding Assistance: Can't understand a parameter or logic? No need to open a browser and browse through documentation. Just ask and get development suggestions and code examples, keeping the coding process uninterrupted.
Practical Demo: What It Can Do For You
We demonstrate four real interaction scenarios here, showing how it transforms natural language into "executable logic":
1. Structural Adjustment: Modify Pipeline with One Sentence
User: "Please help me modify the current Pipeline to add a Citation module for fact-checking the generated content."
2. Scenario Adaptation: Targeted Prompt Optimization
User: "I need to optimize the current Prompt for the legal domain. Please adjust the prompt so that the generated answers are more professional and accurate in terms of terminology and logical reasoning in this field."
3. Configuration Adjustment: Easily Modify Underlying Parameters
User: "I want to switch the generation backend configuration. Please change the generation model backend to OpenAI, change the model name to qwen3-32b, and the API service is deployed on port 65503."
4. Free Tuning: Shortcut from Concept to Implementation
User: "I want to reference this paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.08821 (DeepNote), to redesign my RAG pipeline. Please analyze the core ideas in the article and help me build a similar Pipeline architecture."